
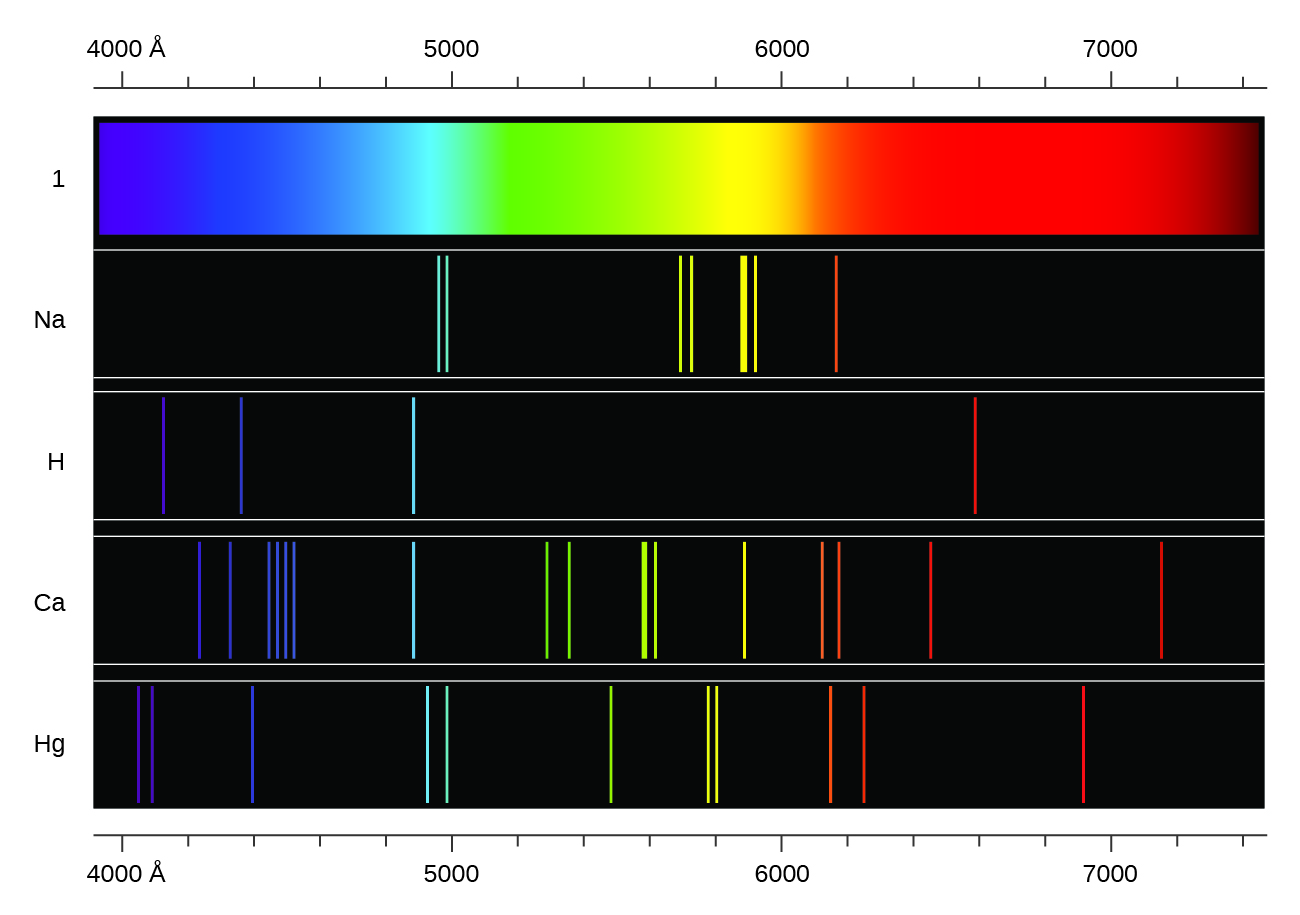
The Figure below shows the atomic emission spectrum of hydrogen. When light travels from one medium to another, it either bends towards the normal or away from the normal. We all know about the refraction of light. In astronomy, the emission spectrum generally. An atomic emission spectrum is the pattern of lines formed when light passes through a prism to separate it into the different frequencies of light it contains. Atomic spectra is the study of atoms (and atomic ions) through their interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Image from the Rochester Institute of Technology, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0. Each thin band in each spectrum corresponds to a single, unique transition between energy levels in an atom. The emission spectrum of burning fuel or other molecules may also be used to example its composition. The atomic emission spectra for various elements. (b) Images of the emission and absorption spectra of hydrogen are shown here. (a) When a hydrogen atom absorbs a photon of light, an electron is excited to an orbit that has a higher energy and larger value of n. An emission spectrum is unique to each element. Figure 7.3.6: Absorption and Emission Spectra. Gaussian fit to the data (black dotted line). Inset: magnified peak of the emission line at 546.0735 nm (literature value, entrance slit approx. Data points (blue), literature peak positions of atomic emissions (red). An additional chemical interference results from self-absorption. In chemistry, an emission spectrum refers to the range of wavelengths emitted by an atom or compound stimulated by either heat or electric current. Atomic emission spectrum of a mercury vapour lamp as measured with the DIY CzernyTurner spectrometer. The figure below shows the atomic emission spectrum of hydrogen. Instruments may contain as many as 48–60 detectors.įlame emission is subject to the same types of chemical interferences as atomic absorption they are minimized using the same methods: by adjusting the flame’s composition and by adding protecting agents, releasing agents, or ionization suppressors. An atomic emission spectrum is the pattern of lines formed when light passes through a prism to separate it into the different frequencies of light it contains. The excess energy can be provided by heat, light, or electrical discharge. However, electrons can be excited to high energy states when they absorb excess energy. Such an atom is said to be in the ground state. When exploding fireworks, you will see the color when the metal atoms absorb energy from the detonater.\). Schematic diagram of a multichannel atomic emission spectrometer for the simultaneous analysis of several elements. Electrons in atoms normally occupy the lowest energy states possible.The spectroscopic data may be selected and displayed according to wavelengths or energy levels by choosing one of the following options: Spectral lines and associated energy levels displayed in wavelength order with all selected spectra intermixed or in multiplet. (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 Christopher Auyeung via CK-12 Foundation) Welcome to the NIST Atomic Spectra Database, NIST Standard Reference Database 78. Atomic and molecular emission and absorption spectra have been known for over a century to be discrete (or quantized).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
